Ethereum Wallet Metamask Fiasco Recap: Google Mistakenly Leaves Scam App on Store
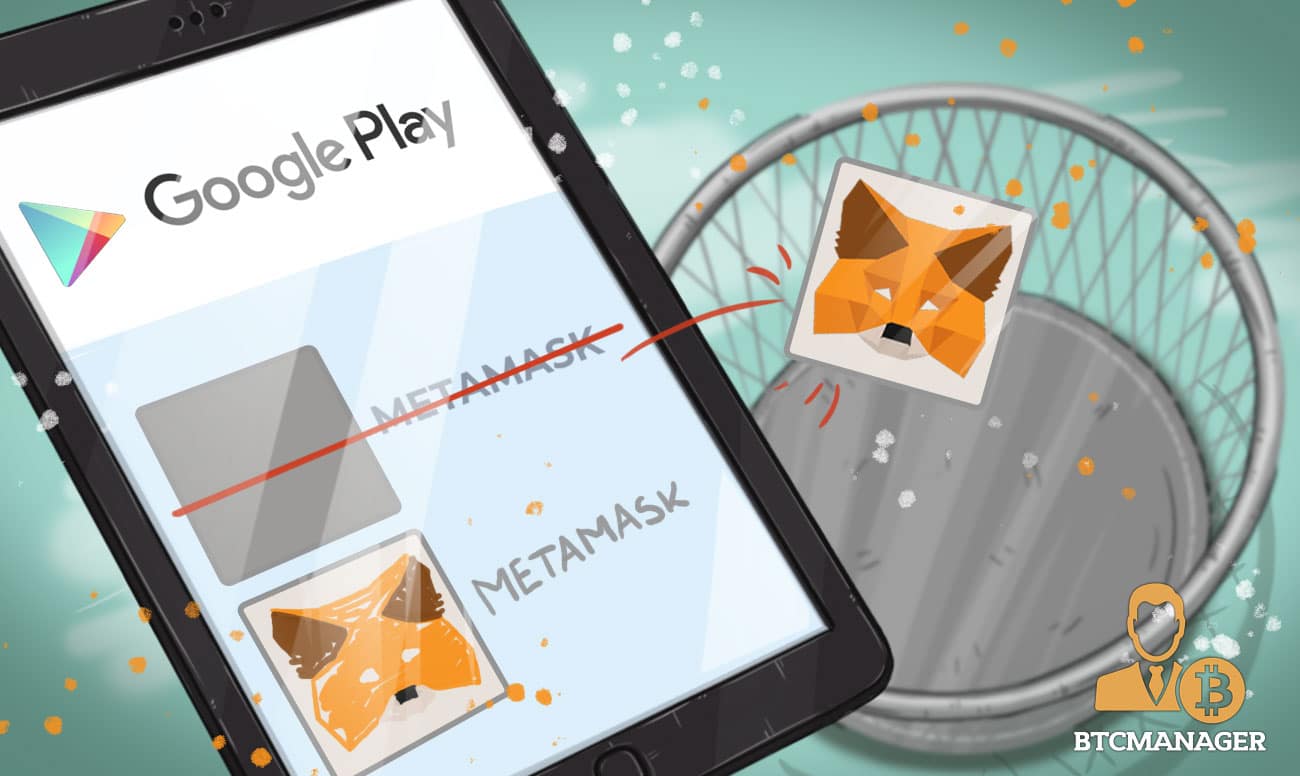

On July 25, 2018, the Google Chrome App Store, a platform that enables users of the most widely utilized web browser in the world to install native browser apps, removed Ethereum wallet MetaMask from its store.
As a popular open-source and non-custodial Ethereum wallet integrated into significant browsers including Google Chrome, FireFox, and Brave, MetaMask has been the go-to wallet for decentralized application (dApp) users on Ethereum, mostly due to its simplistic user interface that allows users to initiate transactions on the Ethereum main chain with minimal effort.
Augur and Brave Step Up
Evidently, the unforeseen removal of MetaMask from the Google Chrome App Store led the cryptocurrency community and the MetaMask development team to panic, and as MetaMask developer Kevin Serrano explained in the company’s official statement, the team was primarily concerned about the presence of MetaMask replicas on the Google Chrome App Store, which had the potential steal funds from new users that could have mistakenly downloaded fake apps instead of the original MetaMask wallet.
The development team of Augur, a rapidly growing decentralized prediction marketplace based on the Ethereum network, initially warned users in the Ethereum community to avoid downloading MetaMask replicas on the Google Chrome App Store.
The Brave Browser team, which also integrated MetaMask earlier this year, warned users to be aware of the situation and prevent downloading fake MetaMask wallets on the Google Chrome App Store.
In its official statement published on July 26, 2018, the MetaMask team stated that it was particularly concerned about newcomers downloading fake wallets on Google and allocated all of the company’s efforts in ensuring that the community is well aware of the case.
“Phishing — although the majority of new users will visit our landing page first or be directly linked to the extension listing (both of which would eventually lead to a dead link), the existence of lookalikes on the storefront page meant that people searching for the extension could be misleading. Additionally, we were alerted of several other phishing vectors on Telegram and on the Google Play Store that was active at that time,” Serrano explained.
Update and What Happens Next
Fortunately, after six hours of being delisted on the Google Chrome App Store and arbitrators on Google confirming the delisting of MetaMask to be an error on the part of Google, MetaMask was restored, with all operations back to normal.
More importantly, the MetaMask team confirmed that MetaMask replicas and fake wallets that have the potential to steal user funds and scam Ethereum holders had been removed from Google.
The team said:
“The most egregious lookalike on the Chrome Web Store has been removed. The team will have ongoing discussions on future red-alert scenarios and have particular protocols to handle each one. In the most optimistic case, we will share the majority of these red-alert scenarios publicly to increase transparency.”
In essence, the root of the issue of the MetaMask delisting on Google Chrome is strikingly similar to the Twitter fake Bitcoin and Ethereum scam giveaways that have been ongoing since early 2018. Through the utilization of simple tools, centralized platforms like Google and Twitter should be able to spot replica apps and accounts, by merely removing new apps and accounts with the same name, image, and description, to eliminate the possibility of phishing attacks.