BitTorrent: The History of Bitcoin Part 4

You can read Part 3 of the History of Bitcoin series here.
BitTorrent was among the projects that played a significant role in shaping cryptocurrencies before the launch of the first decentralized digital currency, bitcoin. Along with Hashcash, b-money, and bit gold, BitTorrent helped lay the foundation for the digital currency landscape we see today.
This article will delve into BitTorrent and its role in developing cryptocurrency in “The History of Bitcoin” series.
What is BitTorrent?
In April 2001, an American programmer by the name of Bram Cohen released a design for a protocol named BitTorrent. The protocol was made to power a peer-to-peer file sharing system.
Cohen was a programmer who had been introduced to computers at an early age by his father. It is reported that he showcased an in-depth grasp as well as a keen interest in computer programming throughout his childhood.
“In first grade, he flummoxed friends with comparisons of the Commodore 64 vs. the Timex Sinclair personal computers, and was actively programming by age [ten].”
Following his graduation from high school, Cohen was accepted into the State University of New York. He commenced his studies but dropped out in 1995 after two years because he was reportedly bored and unchallenged by the material.
Once out of university, Cohen went in and out of different companies, which were exploring novel ways to use the internet, for about five years. He eventually settled on MojoNation in 2001. MojoNation was a project that was trying to design a system through which users could share encrypted files amongst themselves.
“MojoNation allowed people to break up confidential files into encrypted chunks and distribute those pieces on computers also running the software. If someone wanted to download a copy of this encrypted file, he would have to download it simultaneously from many computers.”
While MojoNation eventually failed, it introduced Cohen to the file-sharing space where he decided to create a better protocol. Cohen left the project to work on his own file sharing protocol, which he launched in the same month of April 2001.
How It Works
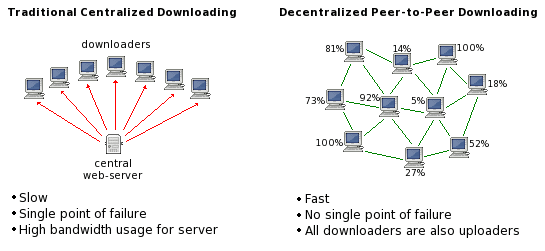
BitTorrent is a peer-to-peer file sharing protocol. It differs from its predecessors as it allows users to access a file from many different sources. This distinction is what enables users to download files much faster. Using the protocol, it is possible to move substantial amounts of data as well as other files such as music and movies over the Internet. The protocol also involves a number of factors.
The first of these is the swarm. This feature is the community of machines that are downloading or uploading content. The next element of the BitTorrent protocol is the tracker. It is a dedicated tool that functions similarly to a search engine. However, it keeps track of the files contained within the swarm and allows users to view as well as quickly access whatever file they may need.
To have access to the swarm and the tracker, one must first download a BitTorrent client. Once this is installed on the computer, it is possible to find and download files. It is important to note that neither the BitTorrent client nor the tracker ever holds the data. Instead, they provide the necessary infrastructure through which the files can be transferred.
(Source: Tixati)
Moreover, the protocol has an inbuilt feature that incentivizes users to participate in the network as file sharers, referred to as “seeders,” as opposed to just downloaders, referred to as “leechers.”
The seeders will experience faster speeds when using the network while leechers will be able to download their files at slower speeds in comparison than the rest of the network.
When the protocol was first launched in 2001, it gained minimal traction. However, by 2004, Cohen had formed a company with his brother Ross Cohen and Ashwin Navin, which he named BitTorrent after the protocol.
Cohen believed it was imperative to create a search engine for the protocol to achieve widespread use. Following the creation of the search engine, BitTorrent became wildly popular and earned the title of the most widely used peer-to-peer file sharing system.
BitTorrent’s Similarities with Bitcoin
BitTorrent and Bitcoin share a few significant similarities. Firstly, both of these protocols operate on a peer-to-peer basis. While this can be said of Bitcoin and other P2P platforms such as MojoNation, BitTorrent stands out because of the way the files are distributed.
As is the case with the Bitcoin ledger, files on BitTorrent are spread out and do not come from only one source. Within the BitTorrent protocol, this feature serves to increase downloading speeds while in the Bitcoin network it serves as a security feature.
Secondly, both Bitcoin and BitTorrent were initially released on an open-source basis. Satoshi Nakamoto, the pseudonymous creator of bitcoin, made the code was visible to all. He also included a detailed paper explaining the software. Similarly, Cohen initially released BitTorrent as an open-source resource. However, this was the case only until version 5.30 of the protocol, after which it was rebranded and became a closed-source software.
Thirdly, both Bitcoin and BitTorrent have been associated with criminal activity. BitTorrent critics believe the protocol is used to violate copyright laws. This criticism is because users can access files like music and movies for which they have not paid. One of the most popular trackers, Pirate Bay, was involved in a lawsuit that resulted in fines and jail time for the platform’s owners.
Comparatively, bitcoin has long been thought of as a tool for criminals. Because bitcoin has been used to pay for goods and services on dark web marketplaces, many critics of the digital currency love to link it to criminal activity.
Lastly, both of these protocols require the Internet to function. Users of both protocols can send data only when they are connected to the Internet.
Recent Interactions with the Cryptocurrency Space
Cohen announced his departure from the BitTorrent company in early 2017 in order to create a cryptocurrency that he believes would function as a more energy-efficient version of bitcoin. The consensus mechanism he proposed is named proof-of-space and is outlined in a white paper called “Beyond Hellman’s Time-Memory Trade-Offs with Applications to Proofs of Space.”
The digital currency is called Chia and is still in development. It is scheduled to be released to the public in mid-2018. In light of Cohen’s experience in the peer-to-peer file sharing space, this cryptocurrency project could be one to watch in 2018.
You can read the entire History of Bitcoin series here.