Vitalik Buterin outlines Ethereum’s countermeasures for quantum attacks

Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin has recently addressed concerns over the potential impact of quantum computing on the Ethereum (ETH) network.
In a post dated March 9 to Ethereum Research, Buterin presented a scenario where quantum computers become accessible and could be used by malicious actors to compromise user funds. He suggested that Ethereum is already prepared to counter such threats with a recovery plan that would involve minimal user impact.
Buterin’s proposition includes the possibility of a “quantum emergency,” where quantum computing capabilities could lead to large-scale theft of Ethereum assets. He outlined a response strategy that involves a hard fork of the Ethereum network. This action would revert the network to a state before the thefts began and would require users to adopt new wallet software designed to prevent future attacks.
The proposed solution hinges on disabling traditional transaction mechanisms in favor of a new transaction type designed to protect against quantum vulnerabilities.
This new transaction type, as detailed in Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP) 7560, relies on Winternitz signatures and zero-knowledge proof technologies, specifically STARKs. These technologies aim to secure transactions against quantum attacks by not revealing the user’s private key during transactions.
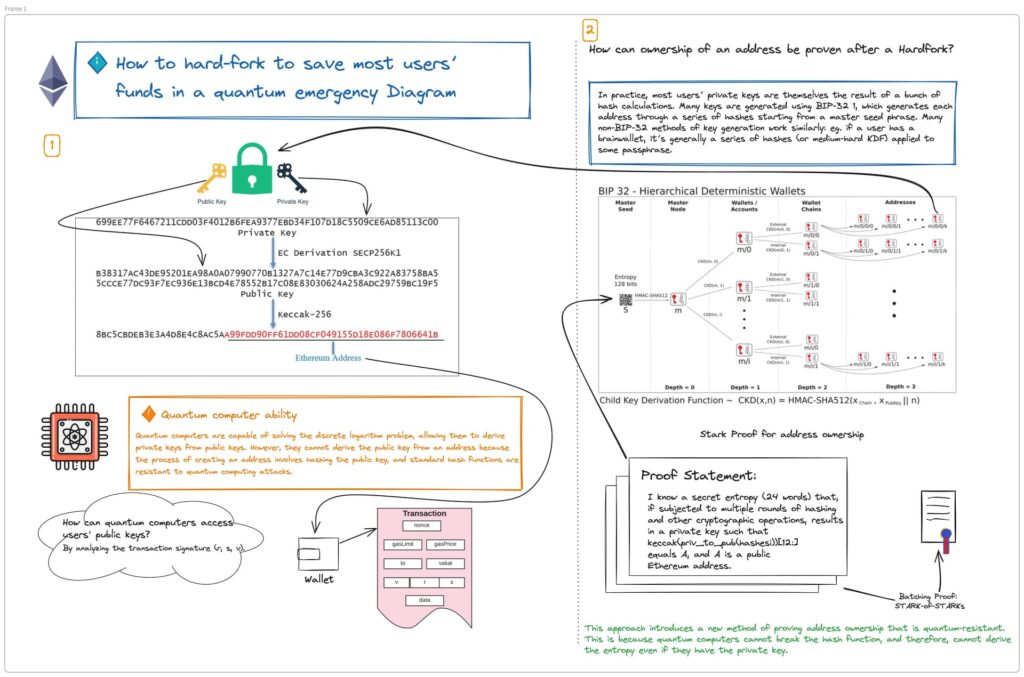
The proposal also introduces ERC-4337 account abstraction for smart contract wallets, enhancing security by preventing private key exposure during the signing process.
Buterin assured that users who have not executed transactions from their Ethereum wallets remain protected, as only their wallet addresses are public. He also mentioned that the infrastructure necessary to implement the proposed hard fork could theoretically begin development immediately.
The discussion around quantum computing and its potential threat to blockchain security is not new. Within the Ethereum community, various solutions and preventive measures have been explored. These include integrating quantum-resistant algorithms, developing early warning systems through machine learning to detect unusual transactions, and employing fail-stop signature schemes to enhance security.
Despite these concerns, the consensus among computer scientists and blockchain developers is that quantum computing capable of breaking blockchain encryption is still several years away, with estimates suggesting a timeframe around 2029. The anticipation allows for ongoing preparation and development of countermeasures to ensure the security of blockchain assets against future quantum computing threats.
The interest in safeguarding Ethereum against quantum computing reflects a broader awareness within the cryptocurrency community of the need to stay ahead in the security arms race. Innovations like Lamport signatures, quantum-resistant smart contract wallets, and the integration of quantum-safe cryptographic measures are part of the efforts to maintain the integrity and trustworthiness of blockchain technology in the face of evolving technological challenges.