What is a rebase token: a guide to elastic tokens

A rebase or elastic token is a cryptocurrency that controls its price by algorithmically adjusting its circulating supply. The expansion and contraction of the token supply are referred to as a rebase mechanism, and thus the term rebase tokens is derived.
Table of Contents
What is a rebase, or elastic, token?
A rebase token functions similarly to a stablecoin. It is pegged to a certain value, usually that of the US dollar. However, instead of utilizing reserves to maintain the price peg, rebase tokens burn circulating tokens or mint new tokens in an automated manner.
In other words, rebase tokens have an elastic supply, with the circulating supply adjusted according to supply and demand. This approach aims to minimize the impact on the value of tokens users hold.
While the supply of a rebase token can be highly volatile, its price is likely to remain relatively steady depending on the price of the underlying asset it tracks.
How do rebase tokens work?
To understand how rebase tokens work, imagine a fictional token called XYZ. Let’s say XYZ has a price target of $1. When the market price of XYZ deviates from this target, the token’s supply automatically adjusts.
Price increase scenario
If the market price of XYZ rises above $1, the rebase mechanism kicks in. The token’s smart contract will proportionally increase each holder’s supply of XYZ tokens. For instance, if you owned 100 XYZ tokens and the supply increased by 10%, you would possess 110 XYZ tokens. Consequently, this dilution keeps the token’s value aligned with the target price.
Price decrease scenario
Conversely, if the market price of XYZ falls below $1, the supply is reduced. In our previous example, if the supply decreased by 10%, your 100 XYZ tokens would become 90 XYZ tokens. This reduction in supply helps counteract the price decline, theoretically bringing it back toward the target.
Rebase cycle
Rebase tokens typically operate on a predetermined rebase schedule, often daily or weekly. During each rebase event, the token’s supply adjusts according to the deviation from the target price. The goal is to create a stable token value that tracks the intended price over time.
When the mechanism adjusts the token supply, it encourages equilibrium between buyers and sellers, driving the token’s price closer to the target price. The adjustment of the token supply affects all holders uniformly, aiming to ensure a fair and proportional distribution of the supply change. This aims to offer a more predictable and stable investment option than traditional cryptocurrencies.
Examples of rebase tokens
Ampleforth (AMPL)
Ampleforth (AMPL) is one of the pioneering rebase tokens. It operates on an elastic supply mechanism, where the token supply expands or contracts daily based on the price deviation from its target value of $1.
The supply adjustments directly impact the number of AMPL tokens held by each wallet, aiming to maintain a stable price over time.
AMPL’s primary goal is to create a digital asset that acts as a reliable medium of exchange and a store of value. By adjusting the supply, AMPL aims to mitigate the effects of volatility and provide a more stable experience for users.

Olympus DAO (OHM)
Olympus DAO (OHM) takes a different approach to rebase tokens by focusing on building a decentralized reserve currency. OHM aims to create a currency with a sound and decentralized monetary policy that can withstand economic uncertainties.
OHM’s rebase mechanism, called “Olympus Pro,” adjusts the token’s supply based on the market’s demand for OHM. By maintaining a flexible supply, OHM strives to achieve price stability and provide a reliable store of value.

Rebase taxes
Rebase taxes are a special tax levied on rebase tokens for various transactions. They serve as a mechanism to regulate and maintain the stability of these tokens.
A purchase tax is levied on the purchase of rebase tokens. This tax is calculated as a percentage of the transaction value and deducted from the buyer’s funds.
The purchase tax helps prevent rapid price fluctuations and discourages excessive purchases, maintaining a balanced supply of tokens.
Similarly, a sales or unwrapping tax is applied when rebase tokens are sold or unwrapped. This tax is deducted from the seller’s or unpacker’s transaction value and protects against sudden spikes in supply caused by large-scale sales or unpackings.
By implementing a sales or unpacking tax, rebase tokens can better control their supply and promote a more stable token ecosystem.
In addition, rebase tokens are often associated with swap transactions, where users exchange one token for another within a decentralized exchange. In such cases, a swap tax is imposed.
This tax is levied on the transaction value, and it helps manage liquidity and mitigate potential market manipulation risks.
Overall, rebase taxes play a critical role in maintaining the stability and sustainability of rebase tokens. By preventing excessive buying, selling, or exchanging, these taxes contribute to a balanced token supply and help create a robust and secure token economy.
Benefits that rebased tokens can give you
Rebased tokens offer a range of benefits that can enhance an investor’s financial strategies and potentially yield positive outcomes.
- Price stability: Rebased tokens aim to maintain a relatively stable price by adjusting the token supply in response to market conditions. When the price deviates significantly from a target value, the token’s supply is increased or decreased to bring the price back in line. This stability can attract users who value predictability and reduce volatility.
- Protection against Inflation: Rebased tokens can act as a hedge against inflation, which occurs when the value of traditional fiat currencies decreases over time due to an increased supply. By adjusting their supply, rebased tokens can help maintain their purchasing power and protect against the erosion of value caused by inflationary pressures.
- Liquidity provision: Users can earn rewards through rebased tokens by participating in liquidity pools or staking programs. It incentivizes participants to contribute to the liquidity and stability of the token’s ecosystem.
- Opportunities for trading: Rebased tokens can create opportunities for traders to profit from price discrepancies. The periodic supply adjustments can result in price imbalances, presenting traders with chances to buy low and sell high as the token rebases to its target value. It can attract traders looking for short-term profit opportunities.
- Experimental and innovative nature: Rebased tokens often represent innovative approaches to token design and economic models. They allow developers to explore alternative crypto stability, liquidity, and governance methods. Participants in these projects can be at the forefront of experimentation and witness the evolution of decentralized finance.
Rebase token risks
Despite their potential benefits, rebase tokens also carry risks that investors and participants should know about. Understanding these risks is crucial for making informed decisions:
- Volatility: Rebase tokens, in their pursuit of price stability, can experience increased volatility during rebasing. Supply adjustments can cause sudden price fluctuations, leading to potential losses for traders and investors unprepared for or unaware of these dynamics. This volatility risk is amplified if market conditions are highly unpredictable or external factors influence the token’s price.
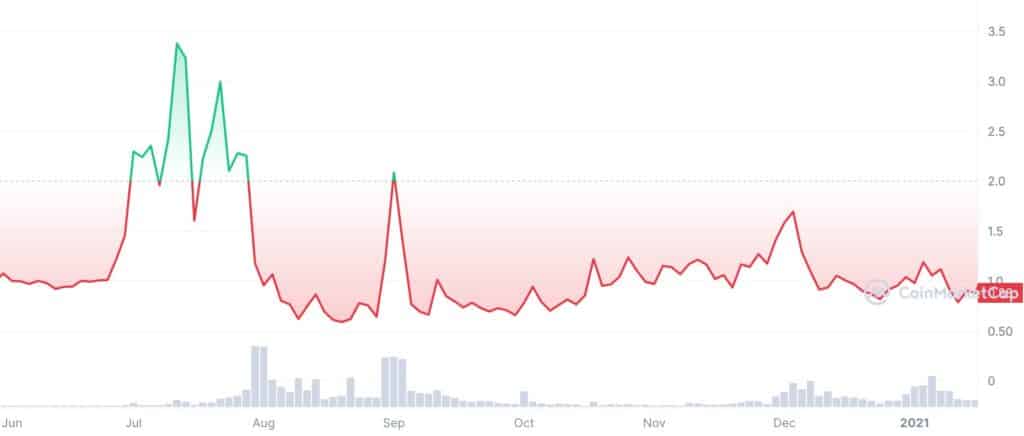
An example of such volatility was seen in July 2020, when AMPL prices tanked by more than 75% in three days. In August of the same year, AMPL dipped again, losing about 66% of its value during rebasing.
- Complex economics: The underlying mechanisms and economic models of rebase tokens can be intricate and challenging to comprehend fully. The rebasing process relies on sophisticated algorithms, accurate market data, and precise calculations. Any errors or flaws in these systems can have severe consequences, leading to unexpected outcomes and a potential loss of value.
For instance, a rebase project called Yam Finance (YAM), which once boasted $600 million in total value locked (TVL), was forced to audit and relaunch itself following issues with its rebasing mechanism that caused more YAM tokens to be minted than was intended.
- Market manipulation: The nature of rebase tokens, with their reliance on supply adjustments, can make them susceptible to market manipulation. Unscrupulous actors may exploit the rebasing mechanism to artificially influence the token’s price or exploit price discrepancies during rebasing. Such manipulation can lead to significant financial losses for unsuspecting participants.
- Regulatory and legal uncertainty: The rapidly evolving regulatory landscape surrounding cryptocurrencies adds another layer of risk to rebase tokens. Regulatory actions or legal uncertainties can impact the viability and operation of these tokens. Participants should be aware of the potential legal and regulatory risks associated with rebase tokens, including possible restrictions, enforcement actions, or changes in legislation.
- Limited track record: Rebase tokens are relatively new in cryptocurrency and have a limited long-term track record. The lack of historical data and market cycles makes it challenging to assess their performance and reliability over extended periods. Before engaging, participants should consider the token’s track record, the team behind it, and the project’s overall credibility.
FAQs
What is a positive and negative rebase token?
A positive rebase token adjusts its supply to increase when the price exceeds a target, rewarding holders. A negative rebase token reduces its supply when the price falls below a target, aiming to stabilize its value. Both types aim for price stability through supply adjustments.
Are rebase tokens a good Investment?
Investing in rebase tokens has potential benefits. You can take advantage of price movements and potentially earn profits. You can also support projects that aim to address volatility problems in the market. Rebase tokens provide an opportunity to explore innovative ideas and participate in decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems.
However, investing in rebase tokens carries inherent risks. These tokens are highly experimental and can be subject to extreme price volatility. The rebase mechanism may not always work as intended, leading to unexpected outcomes.
Additionally, the market for rebase tokens is relatively new and lacks the same level of stability and liquidity found in more established assets.
Are rebase tokens taxable?
Typically, yes. Unless you live in a jurisdiction without income, wealth, and/or capital gains tax, you will have to tax your investment returns. Please check with a tax advisor to ensure you are taxing your crypto investment income accordingly.