What is Base? Unpacking Coinbase’s new layer-2 network and its impact
Base, Coinbase’s new layer-2 blockchain network, was built to enhance Ethereum’s capacity for decentralized applications, improve user interfaces, and reduce transaction costs. Let’s explore how it works, its implications, and its challenges.
On Aug. 9, Coinbase, a leading player in the cryptocurrency market, launched its Base layer-2 blockchain network.
Far from a mere technical upgrade, this development has been marked by both anticipation and scrutiny. With promises of improved decentralized applications (dApps) on Ethereum (ETH), reduced transaction costs, and enhanced interfaces, the launch of Base has sparked curiosity and debate.
How does Base work?
Coinbase’s Base is a new entrant in the burgeoning layer-2 blockchain network arena, with a focus on enhancing the dApp ecosystem on Ethereum.
Base positions itself as a solution to increase efficiency and improve user interfaces, but how does it intend to achieve these goals?
Base leverages the OP Stack, an open-source technology that provides a base for deploying optimistic rollups. It processes transactions off the main Ethereum chain, consolidating them into batches before transferring them back.
The attributes of Base extend to inheriting Ethereum’s renowned security protocols, alongside claims of providing faster transactions at lower costs. Moreover, it’s fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
However, these features aren’t exclusive to Base. Other market-leading layer-2 solutions, such as Arbitrum (ARB) and Optimism (OP), provide similar offerings.
Despite being relatively new in the field, Base has quickly established itself, ranking among the top Ethereum’s layer-2 solutions in terms of total value locked (TVL) at around $200 million.
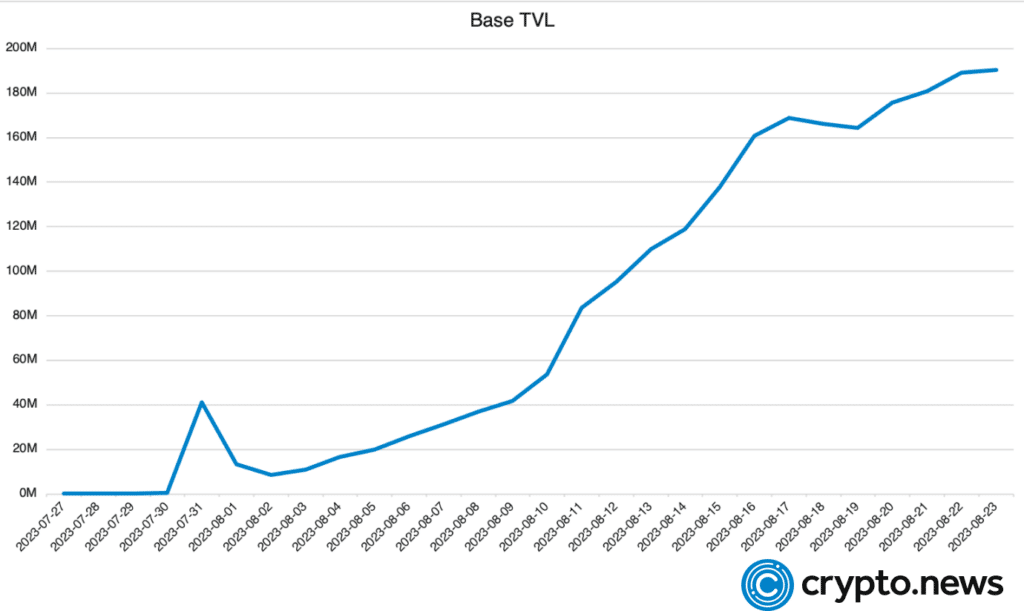
Interestingly, Base has managed to achieve this without introducing a unique supporting token, instead opting to use ETH as the payment medium for transaction fees.
Base launch and early strategy
The launch was accompanied by various events across different fields, such as art, gaming, and music. One of these events included minting non-fungible tokens (NFTs) on the Base network, generating huge revenue through sales.
While such initiatives may point to a comprehensive plan to foster broader adoption, they simultaneously prompt inquiries about the user experience, potential for organic growth, and how Base intends to carve out its unique niche in the competitive landscape of existing solutions.
In summary, Base presents itself as an innovative layer-2 solution with the ambition to redefine how dApps operate on Ethereum. By employing unique frameworks and engaging the community in diverse ways, it has made a promising start.
Pros and cons of Base chain
As the blockchain community continues to assess Base chain, its various features and challenges are coming to light. Below, we will explore Base’s advantages and potential drawbacks, providing a comprehensive overview of this new player in the layer-2 arena.
Pros
- Accessible: Base chain’s compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) makes it an attractive option for users and developers. Since it’s built on the same architecture as Ethereum, existing dApps and smart contracts can easily be ported over to the network without requiring significant modifications.
- Low cost: One of Base’s standout features is its low-cost transaction structure. Like most optimistic rollups, it’s designed to dramatically reduce gas fees, with transactions often costing just a few cents. This makes it appealing for those looking to perform regular transactions without incurring heavy costs.
- Secure and scalable: By leveraging Ethereum’s well-established security protocols and combining them with layer-2 transaction speeds, Base provides a network that’s both secure and capable of handling increased transaction volume. This dual focus on security and scalability makes it a promising solution for dApps needing to handle a large number of transactions.
- Backed by Coinbase: As a product of Coinbase, one of the most recognized and financially robust companies in the crypto space, Base benefits from strong backing and resources. This association provides credibility and ensures substantial support for the growth and development of the Base Chain.
Cons
- Unproven: Since Base is a new entrant in the blockchain space, its architecture and overall stability have not yet been tested extensively. This lack of real-world validation may cause some hesitation among potential adopters and could lead to unforeseen challenges as the platform matures.
- Competition: The layer-2 field is highly competitive, with established solutions like Arbitrum and Polygon (MATIC). These rivals have already gained traction and recognition, making Base’s path to dominance more challenging. Its success will likely depend on how well it can differentiate itself from these well-established competitors.
- Centralization concerns: Though Base chain has expressed a commitment to progressive decentralization, its connection with Coinbase has raised some concerns about potential centralization. As a product of a major corporation in the crypto space, there could be apprehensions regarding the control and governance of the network, potentially impacting its perception as a truly decentralized solution.
Base chain’s early success and challenges
Base Chain’s mainnet has already made waves in the crypto community by registering a significant number of daily transactions.
According to Dune Analytics, on August 21, Base reached the mark of 1.27 million daily transactions, surpassing other notable layer-2 networks like Arbitrum (558k) and OP Mainnet (405k).
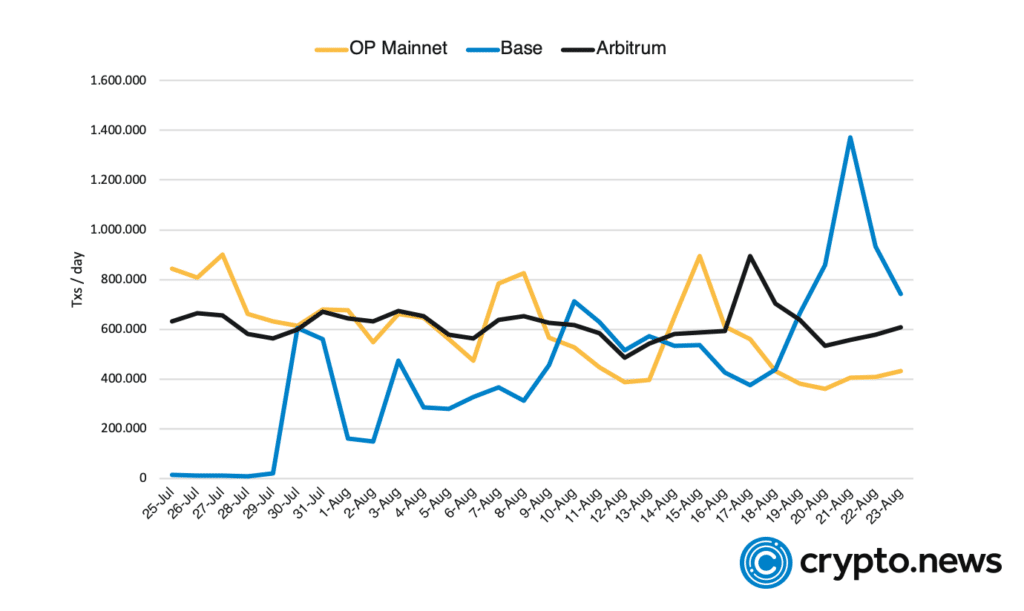
In comparison, Ethereum’s base layer averages about 1 million daily transactions. Such a feat so quickly after launch certainly piqued interest in Base and its potential.
A significant factor driving Base’s transaction volume has been the popularity of Friend.tech, a decentralized social media platform built on Base.
This new platform has exploded with popularity, in part because it allows users to buy and sell shares of their friends’ social profiles, a concept that has been embraced by celebrities.
While Base’s transaction numbers are impressive, Ethereum researcher Evan Van Ness and Flashbots product lead Robert Miller have pointed out signs that a substantial portion of transactions may be coming from bots and spammers.
These entities might be attempting to gain an edge on Friend.tech, casting a shadow on the authenticity of the transaction volume. The extent to which this activity affects the platform’s reputation and growth will require careful monitoring.
Base and scam tokens
Since its introduction in August, Base has not been without its challenges. The openness and accessibility of the network, attributes typical of blockchain networks, have led to unintended consequences.
Developers, exploiting vulnerabilities in the network, have managed to create over 500 scam tokens. Solidus Labs, a New York-based crypto market integrity platform, estimates that these fraudulent activities have allowed scammers to make off with roughly $2 million, Bloomberg reported.
These deceptions vary in nature; around 300 of the scam tokens were created to mint an unlimited number of coins without the knowledge of Base’s users, while another 60 were structured to block buyers from reselling them on exchanges.
The negative impact of these scam tokens extends further. They’ve led to approximately $3.7 million in trading volume on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) operating on Base, where users typically trade directly with one another.
The situation has been further exacerbated by the false promotion and trading of other cryptocurrencies on Base, deepening the concerns over security and integrity.
Such security lapses aren’t unique to Base but are emblematic of broader challenges within the blockchain space. The very characteristics that make these networks appealing – their openness and the ability for anyone to participate – also make them prone to abuse.
The road ahead
The road ahead for Base is laden with potential and fraught with complexities. The early successes, technological promise, and Coinbase’s backing place Base in a strong position to make a lasting impact in the layer-2 ecosystem.
Yet, the challenges of security, competition, decentralization, community development, and regulation loom large.
How Base navigates these challenges and capitalizes on its opportunities will define its trajectory in the coming months and years. As a new entrant in a dynamic and competitive field, Base’s actions, decisions, and agility will be closely watched by the crypto community and industry stakeholders.
The stage is set for Base to either become a transformative force in dApps or a cautionary tale in the turbulent world of blockchain innovation.