What is sharding in crypto?

Sharding is a technique that involves breaking down a larger database or ledger into smaller partitions known as shards. This approach is aimed at improving network scalability and transaction speed. So, in simple terms, sharding in crypto refers to the process of dividing a blockchain into smaller and more manageable segments.
Sharding definition
Sharding in the context of crypto refers to a technique used to improve the scalability and performance of blockchain networks.
Imagine a blockchain as a big ledger containing all the transaction history. Sharding allows breaking down this ledger into smaller, more manageable pieces called “shards.”
Each shard is like a mini-ledger that stores a subset of the entire transaction history, along with account balances and smart contracts. By dividing the workload across multiple shards, the blockchain network can process transactions in parallel, boosting overall throughput and reducing transaction confirmation times.
How does sharding work?
Here’s an analogy to help grasp the concept of crypto sharding: think of a large library with a single librarian handling all the requests and transactions. Sharding would involve dividing the library into multiple sections, each with its librarian. When someone wants to borrow a book from a particular section, they can approach the librarian responsible for that area rather than waiting for the main librarian. This approach speeds up the process and enables multiple borrowers to access different sections simultaneously.
Blockchain sharding works similarly. Instead of a single, centralized database, the blockchain network is divided into smaller parts, each capable of processing transactions independently. This distribution of work helps increase the network’s capacity to handle more transactions at the same time, making it more scalable and efficient.
Horizontal partitioning
It is important to know that crypto sharding involves horizontal partitioning instead of vertical partitioning. Each shard contains some data present in other shards, but it is specifically designed to hold unique data accessible only through it. To utilize and access the data, one needs to target the particular shard containing the desired information.
Sharding is utilized in database architecture to enhance the performance of databases and search engines. By reducing the index size of a ledger, this design technique enables quicker search results.
Moreover, since different shards can be stored on separate servers, sharding proves beneficial for large corporations with extensive datasets that require separate storage, such as multinational corporations operating in multiple countries.
Sharding in distributed ledgers
Sharding has grown in popularity within the cryptocurrency community as a result of widespread concerns over blockchain scalability issues. For instance, the Bitcoin network processes about seven transactions per second, and Ethereum is only slightly faster, handling around 13 operations per second. These are both paltry compared to large payment processors like Visa and Mastercard.
While the Bitcoin community has dealt with its scaling issues in various ways, the Ethereum project has outlined a more streamlined approach to solving its scalability concerns. Ethereum has switched to a proof-of-stake (PoS) algorithm, which will work in tandem with a sharded database design.
Sharding examples
Sharding has been successfully implemented in various blockchain projects. Let’s explore a few notable examples:
Zilliqa
Zilliqa is a blockchain platform explicitly designed with sharding in mind. It employs a technique known as “network sharding” to divide the network into multiple smaller groups of nodes. Each shard operates as an independent mini-blockchain, capable of processing its transactions and smart contracts, enabling higher transaction throughput.
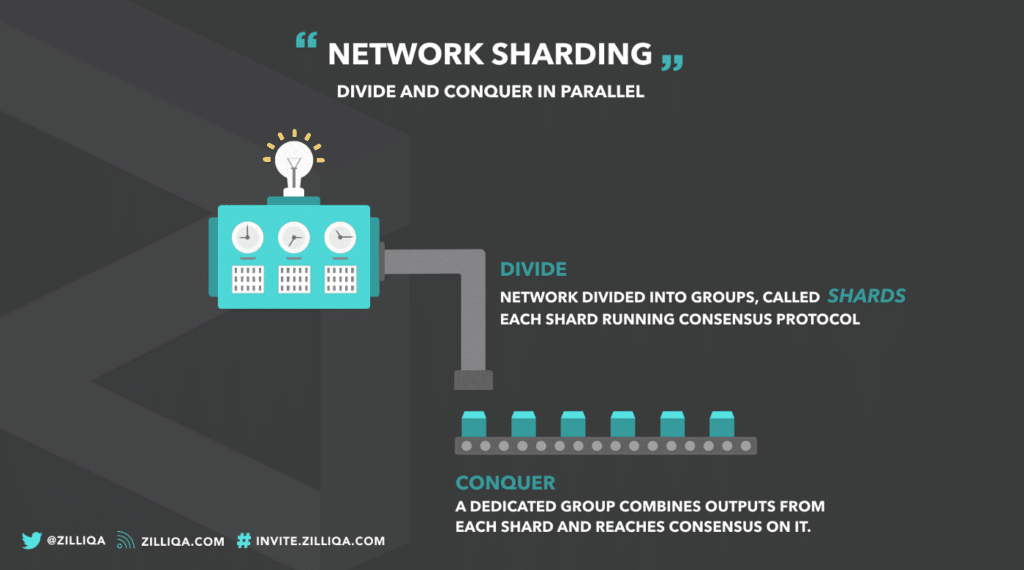
To ensure consensus among the shards, Zilliqa utilizes a consensus mechanism called Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT). In this system, a small group of nodes, known as the DS Committee, is responsible for validating transactions and maintaining consensus within each shard. The DS Committee is dynamically elected based on a combination of proof of work (PoW) and proof of stake (PoS) mechanisms.
To prevent security vulnerabilities, Zilliqa also incorporates cross-shard communication. When a transaction involves multiple shards, it is divided into smaller pieces and processed simultaneously across the relevant shards. This is made to enable efficient coordination and to ensure the consistency of the blockchain state across all shards.
Harmony
Harmony is another blockchain platform that utilizes sharding to enhance scalability and throughput. It employs a technique called “state sharding,” where the entire network is divided into shards, with each shard maintaining its own set of account balances and smart contracts.
To ensure consensus and security across shards, Harmony implements a consensus protocol called Effective Proof-of-Stake (EPoS). EPoS relies on a committee of validators who are randomly assigned to shards. These validators propose and validate blocks within their respective shards, ensuring agreement on the order of transactions and preventing double-spending.
Harmony further enhances its sharding mechanism with a technique called cross-linking. It involves periodically creating checkpoints that connect shards and store them on the main chain. This process aims to ensure the integrity and consistency of the entire blockchain, as these cross-links serve as reference points for shard states.
Additionally, Harmony employs a feature called “Fast Byzantine Fault Tolerance” (FBFT) within each shard. FBFT enables fast and efficient consensus within a shard by reducing the number of required message exchanges among validators.
QuarkChain
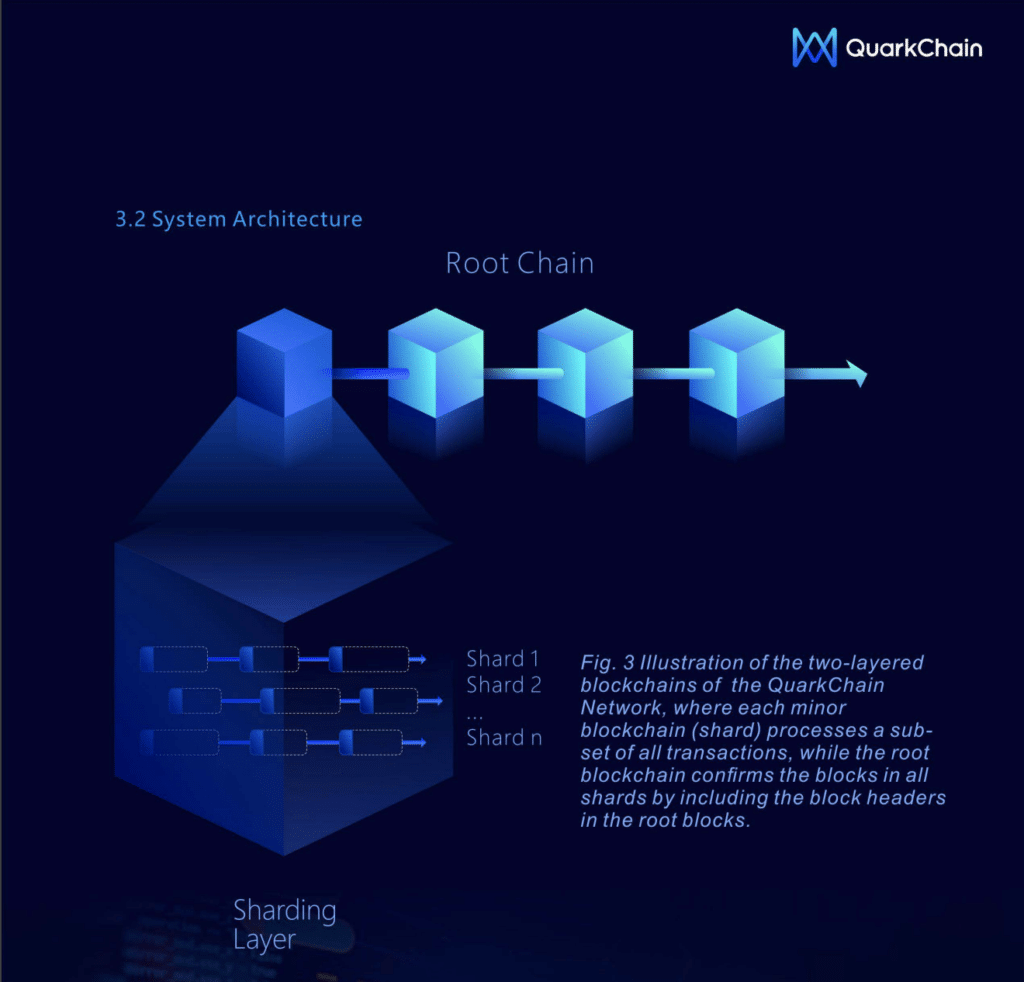
QuarkChain is a blockchain project that aims to reach more than 100,000 TPS. Its technique divides the network into multiple shards, each capable of processing transactions independently.
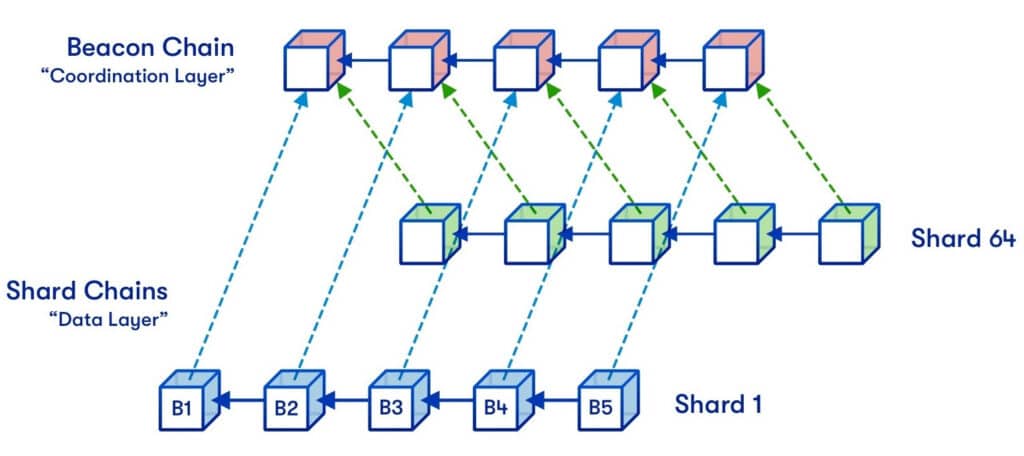
These shards are organized in a two-layer structure, consisting of the root chain and the shard chains. The root chain is responsible for reaching consensus on the state of the entire network, while the shard chains process transactions within their respective shards.
How would sharding work on Ethereum?
The Ethereum network is actively exploring sharding as a potential solution to overcome its scalability challenges. To that end, the Ethereum Improvement Proposal 4844 (EIP-4844) introduced “Proto-Danksharding,” a highly anticipated sharding upgrade slated for the network in around 2023. The update aims to make transactions on Layer 2 cheap and to scale Ethereum to more than 100,000 transactions per second (TPS).
Proto-Danksharding was proposed by researchers Protolambda and Dankrad Feist to improve the scalability of Ethereum’s rollups.
Currently, rollups face limitations in making transactions cheaper. Rollups is a scaling system that groups transactions off-chain and then posts them in calldata (data sent with Ethereum transactions), which is processed by all Ethereum nodes and stored on the chain permanently.
Proto-Danksharding aims to solve this issue by using data blobs that can be sent and attached to blocks. They are not accessible to the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and are automatically deleted after a fixed period of time (1-3 months). It allows rollups to send their data at a much lower cost, enabling them to offer cheaper transactions to end users.
Proto-Danksharding does not fit into the traditional sharding meaning of splitting the blockchain into multiple parts. Instead, it utilizes distributed data sampling across blobs to scale Ethereum. This simpler implementation model is sometimes referred to as “data-sharding.”
The full realization of the roll-up scaling started by Proto-Danksharding aims to provide ample space on Ethereum for rollups to store their compressed transaction data. This advancement could enable Ethereum to easily support numerous individual rollups and pave the way for achieving millions of transactions per second.
With the transition from Proto-Danksharding to full Danksharding, Ethereum plans to expand the number of blobs attached to blocks from 1 to 64. Other changes include updates for consensus clients to make it possible for them to handle these larger blobs. Some of these changes are already part of the Ethereum roadmap.
While full Danksharding is still a few years away, Proto-Danksharding is expected to arrive relatively soon in the second half of 2023.
FAQs
What does sharding mean in crypto?
In the world of cryptocurrency, sharding refers to a technique used to enhance the scalability and performance of blockchain networks. It involves dividing the blockchain into smaller, more manageable parts called shards. Each shard operates independently and processes a subset of the network’s transactions and smart contracts.
What are the disadvantages of sharding in blockchain?
Complexity: Implementing sharding requires modifying the underlying infrastructure and consensus mechanisms, which can be complex and time-consuming, causing delays in development and deployment.
Impact on decentralization: Sharding divides the network, limiting access to the complete blockchain history and raising concerns about data availability and trust.
Smart contract and cross-shard complexities: Interactions between shards and designing multi-shard smart contracts can be challenging and require careful consideration.
Communication overhead: Coordinating transactions and maintaining consensus across shards requires additional communication among nodes, potentially resulting in higher latency and reduced performance.
What are the benefits of sharding in crypto?
Improved scalability: Sharding involves dividing the network into smaller partitions, with each processing its own subset of transactions. This parallel processing significantly increases the network’s capacity to handle a larger number of transactions simultaneously, enabling faster transaction confirmations and a higher throughput overall.
Enhanced performance: Since each shard operates independently, the computational burden is distributed, reducing the congestion and latency that can occur in traditional blockchain architectures. This results in faster transaction processing times and a smoother user experience.
Lower transaction fees: With increased scalability and improved performance, more transactions can be processed within a given timeframe. It reduces competition for block space and alleviates the demand-supply gap, resulting in reduced fees for users.
Enhanced security: In a sharded system, each shard processes only a subset of transactions, making it more difficult for malicious actors to compromise the entire network. Sharding also enables faster consensus mechanisms, reducing the window of opportunity for attackers to manipulate transactions or disrupt the network.
Which crypto uses sharding?
Examples of cryptocurrencies utilizing sharding include Polkadot (DOT), Elrond (EGLD), Near (NEAR), Zilliqa (ZIL), Harmony (ONE), QuarkChain (QKC), and Multivac (MTV).
Does Ethereum 2.0 use sharding?
There are plans for Ethereum 2.0 to utilize sharding to address its scalability challenges. The network is going to implement an upgrade called “Proto-Danksharding.” It aims to enhance Ethereum’s scalability specifically for rollups, which currently are limited in reducing transaction costs.
Proto-Danksharding doesn’t follow the traditional sharding meaning of splitting the blockchain into multiple parts. Instead, it uses distributed sampling across data “blobs”, in a process often referred to as “data-sharding.”